AA2 Week 4 - Game Engine Overview [1]
[1]
As you know, my post-2000 game I am analyzing is Unreal Tournament. This being the original version which I find more fun than the 2004 release. The upcoming 2007 release looks to be good on the trailer but I obviously haven't played it yet. [3]
[2]
Unreal Tournament 2007 looks like a cool game
There is a point for all this rambling. That is since all the Unreal releases are based on the Unreal Engine licenced by Epic Games. This engine was first released in the game Unreal in 1998. The engine has had subsequent versions for each release of Unreal Tournament
The original engine that was used for Unreal was also used for Unreal Tourament. Unreal Tournament was released between the end of 1999 or beginning of 2000 (depending on which country you live in).
Unreal and Unreal Tournament have been the basis for games with similar characteristics:
Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six 3: Raven Shield
Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six: Vegas
Red Steel
Gears of War
Since then the engine has also been used for future games including:
* Adventure Pinball: Forgotten Island — (2001) Digital Extremes
* Brother Bear — (2003) KnowWonder Digital Mediaworks
* Clive Barker's Undying — (2001) Dreamworks Interactive
* Deus Ex — (2000) Ion Storm
* Deus Ex: The Conspiracy — (2002) Ion Storm
* Dr. Brain's Thinking Games: Action/Reaction — (1999) Knowledge Adventure
* Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets — (2002) KnowWonder Digital Mediaworks
* Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone (Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone in the U.S) — (2001) KnowWonder Digital Mediaworks
* Mobile Forces — (2002) Rage Software
* Nerf Arena Blast — (1999) Visionary Media, Inc.
* New Legends — (2002) Infinite Machine
* Rune — (2000) Human Head Studios
* Rune: Halls of Valhalla — (2001) Human Head Studios
* Rune: Viking Warlord — (2001) Human Head Studios
* Star Trek: Deep Space Nine: The Fallen — (2000) The Collective
* Star Trek: The Next Generation: Klingon Honor Guard — (1998) MicroProse
* Tactical Ops: Assault on Terror — (2002) Kamehan Studios
* TNN Outdoors Pro Hunter — (1998) DreamForge Intertainment
* Twin Caliber — (2003) Rage Software
* Unreal — (1998) Epic Games
* Unreal Mission Pack: Return to Na Pali — (1999) Legend Entertainment
* Unreal Tournament — (1999) Epic Games
* Unrealty — (2000) Perilith Industrielle
* Virtual Reality Notre Dame: A Real Time Construction — (1999) Digitalo Studios
* The Wheel of Time — (1999) Legend Entertainment
* X-COM: Enforcer — (2001) MicroProse [4]
[4]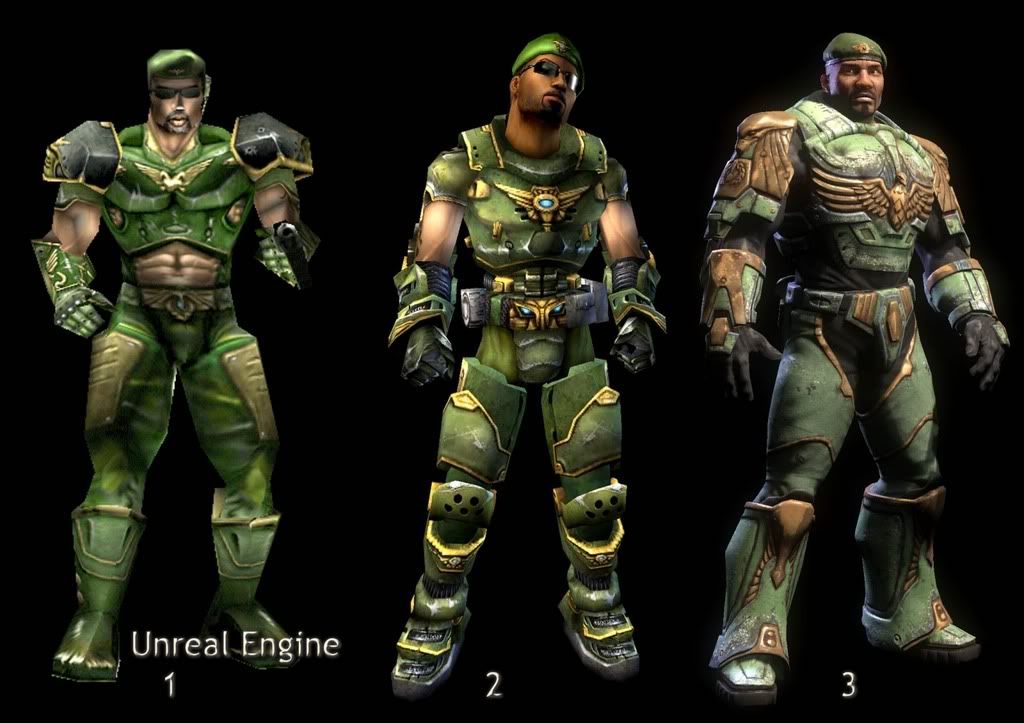
A comparison of Unreal Engine 1, 2 and 3's rendering capabilities using the Malcolm model from Unreal Tournament, Unreal Tournament 2004 and Unreal Tournament 3 side-by-side. As you can see, the graphic capabilities have come a long way.
There are three versions of the Unreal Engine but the game I am focusing on utilizes the first Unreal Engine. In terms of finding information on the Audio Engine for Unreal Tournament, it was actually quite hard to find anything at all. I did find an article written by Tim Sweeney, a programmer who worked on the Unreal Engine. He also founded Epic Games.
Digital Sound System
* Supports 3D positioning via distance attenuation, stereo panning, doppler shifting.
* Supports software Dolby Surround sound encoding for full 360-degree panning among the center, rear, left, and right channels (requires a Dolby decoder).
* Supports rich, ambient environmental sounds which can be fully controlled from UnrealScript.
* Advanced software mixer supports up to 64 stereo channels of music and sound, and mixes to a 32-bit buffer internally for maximum sound quality.
* Supports 8- and 16-bit samples using any playback rate from 4 kHz to 44 kHz.
* Dynamic sample interpolation enables high-quality pitch shifting without distortion.
* Optimized to take advantage of Intel's MMX™ technology, with fallback to support regular Pentium® processors.
* Supports DSP-style reverb and echo postprocessing on the sound effect stream.
* Aural raytracing realistically simulates the echo and reverb characteristics of complex environments. When enabled, UnrealEd pre-computes a reverb kernel for each designer-specified zone in the level.
* Supports Microsoft DirectSound and legacy WinMM sound output for backwards compatibility.
* Plug-in interface makes it possible to integrate other sound systems into the Unreal technology.
* Supports Aureal A3D 3D sound positioning, and the upcoming Creative Labs 3D sound cards.
Digital Music System
* Supports both CD audio and realtime digitally mixed music. Game designers can mix and match soundtracks in both formats to take maximum advantage of the speed and quality of CD music and the dynamic music and Internet portability of digitally mixed music.
* Smooth and instantaneous dynamic music changes for fading between songs, fading between tracks within a song, fading to silence, and instantly switching songs.
* Realtime mixing of musical instruments and sound effects.
* Supports volume and panning envelopes for professional composing.
* Supports up to eight octaves per sample.
* Supports all widely used module file formats, including .mod, .s3m, .xm, and .it. [5]
[1]
NICE!
[1] Absolute-Playstation, 'Unreal Tournament'. http://www.absolute-playstation.com/gp2a/unreal_tournament_hr_1.jpg (Accessed 10/8/7)
[2] youtube, Unreal Tournament 2007 Trailer. www.youtube.com (Accessed 10/8/7)
[3] wikipedia, 'Unreal Tournament'. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unreal_Tournament (Accessed 10/8/7)
[4] wikipedia, 'Unreal Engine'. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unreal_Engine (Accessed 10/8/7)
[5] Epic MegaGames, Inc. 'Unreal Technology Features'. http://unreal.epicgames.com/UnrealFeatures.htm (Accessed 10/8/7)
[6] Christian Haines "Audio Arts: Semester 2, Week 4: Game Engine Overview" Lecture presented at the Electronic Music Unit, University of Adelaide, 7th August 2007.
Tuesday, August 14, 2007
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

No comments:
Post a Comment